 With the advances in technology around electric motor testing, the motor inductance testing is now easier to perform than ever. However, there are challenges that remain, and the most difficult issue lies in the lack of hard-set guidance from an independent body as to what constitutes appropriate acceptance standards and criteria.
With the advances in technology around electric motor testing, the motor inductance testing is now easier to perform than ever. However, there are challenges that remain, and the most difficult issue lies in the lack of hard-set guidance from an independent body as to what constitutes appropriate acceptance standards and criteria.
This is a serious problem because inductive imbalance testing can lead to false positives if you do not understand what can influence the test. These false positives can then result in unnecessary repairs or rejection of otherwise acceptable electric motors. And let’s be honest: even new machines don’t meet some of the “guidelines” that can be found online. To that end, we will be discussing inductive imbalance testing and what can influence the results.
What is an Inductive Imbalance Test?
An inductive imbalance test checks for non-symmetrical inductance between the motor’s three phases. It may be performed as part of preventative maintenance, predictive maintenance, and testing after a motor repair.
When used as part of predictive maintenance, inductive imbalance testing contributes to fault zone analysis. Fault zone analysis provides a comprehensive overview of a motor’s health by looking at six specific fault zones: power quality, power circuit, rotor, stator, insulation, and air gap. Inductive imbalance testing is used with the stator fault zone, but inductance is also key to the rotor influence check (RIC) for the rotor fault zone and air gap fault zone.
During this test, a technician applies a high-frequency AC voltage to the motor, which in turn produces a magnetic field around the windings. The inductance for each phase is then measured and compared to the other phases to calculate the motor’s inductive imbalance. The percent of inductive imbalance is then used to determine if the windings between phases are well balanced.
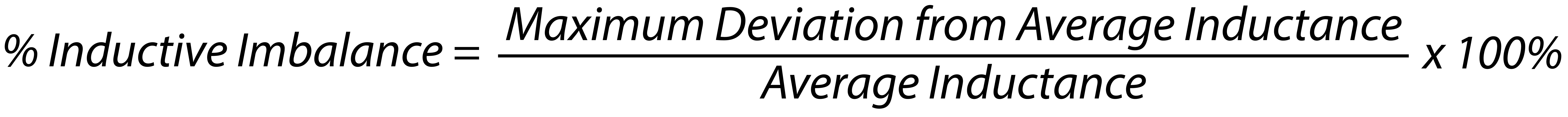
Testing for AC motor inductive imbalance requires EMT (electric motor testing equipment). More specifically, a Predictive Maintenance (PdMA) Motor Circuit Evaluator (MCE) is used. This particular motor testing and evaluation tool can generate extensive results and analysis in a matter of minutes when used by a trained technician.
Why is Inductance Important?
A motor with an unbalanced inductance may be experiencing …
- Motor core and winding degradation
- Issues with the rotor or rotor core
- Problems with rotor position relative to its magnetic center
When an inductance imbalance is present, it can lead to other problems including excessive vibration and current imbalances. Unaddressed, it can cause your motor to be seriously damaged, leading to costly downtime and expensive repairs. However, not all inductive imbalance is the result of serious issues.
What Leads to Inductive Imbalance?
There are a wide variety of elements and variables that make up inductance. Consider this equation:
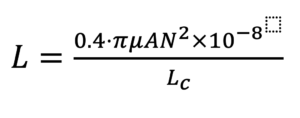
L is inductance, 𝜇 is the permeability of the core material, A is the cross-sectional area of the core (which includes the diameter of the core), N is the number of turns, and Lc is the length of the core. Dimensions, windings, and material properties all contribute to the amount of inductance that is present. In addition, inductance is also affected by the position of the rotor relative to the center bore of the stator.
Just because a motor has a high inductive imbalance does not automatically mean that it should be rejected. There are several factors that can affect the inductive imbalance of a motor, including tests and processes that can leave a residual magnetic flux. This residual flux will create a temporary (notice we said temporary) non-symmetrical inductance between the three phases. Surge and lightning arrestor circuitry and power factor corrections can also impact the results of inductive imbalance testing.
Rotor faults and rotor failure can cause an inductive imbalance between 8% and 15%. This often happens when the rotor has half of the cage shifted at the center of the rotor, and once the rotor is removed, the inductive imbalance can fall to 1%. Stator eccentricity and air gap eccentricity can also lead to inductive imbalance.
Making the Best Call
The general rule regarding inductive imbalance is as follows: it should be below 7% for form wound motors and below 12% for random wound motors. However, as alluded to at the beginning, even new motors may not make the cut with these types of guidelines. When you are setting the acceptance criteria for inductive imbalance tests, there are other factors to keep in mind.
Keep in mind that power factor correction capacitors can affect the results when an inductive imbalance test is performed, as can surge and lightning arrestor circuitry. If present, they should be disconnected from the circuit before initial testing and then reconnected for comparison to see what impact they may have on the results.
To determine if the inductive imbalance is a motor issue, you can isolate the source of the imbalance to the rotor or stator by performing a RIC test with the motor energized and then, after allowing the rotor to warm up, performing that same test again. If this eliminates most of the inductive imbalance, then the problem is most likely not an issue with the motor but the after-effects of a process or test that was performed by the repair shop. In such a case, the imbalance should be recalculated minus the influence of the rotor.
Conclusion
Inductive imbalance testing may be relatively easy to perform, but deciding whether or not a motor should be accepted based on the results is another matter. At HI-Speed Industrial Service, our technicians not only know how to use the latest MCE tools, but they know how to interpret the data, including inductive imbalance. When you send a motor into our shops for repair or use our predictive maintenance (PdMA) services to evaluate in the field, our team will study the inductive imbalance results and track down the source of any imbalance to make sure that a motor is not subject to unnecessary repairs and associated downtime. Contact HI-Speed today to learn what we have to offer in the way of motor maintenance and repair!

